How to Improve Your Core Web Vitals (CWV) for Better SEO Performance
As Google’s search algorithm continues to develop, adapt and evolve, one of the most significant updates in recent years is the introduction of Core Web Vitals. These metrics, introduced to enhance user experience, are now critical factors in determining your website’s search rankings, showcasing the key link between core web vitals and seo.
In this blog post, we’ll look into what Core Web Vitals are, Core Web Vitals impact on SEO, and actionable steps you can take to improve your core web vital scores.
What Are Core Web Vitals?
Core Web Vitals are a set of specific metrics that Google considers essential for an outstanding user experience across all devices and browsers on your website. These metrics are often related to website performance and technical areas of your website which can be improved
The Core Web Vitals tend to focus on three main aspects:
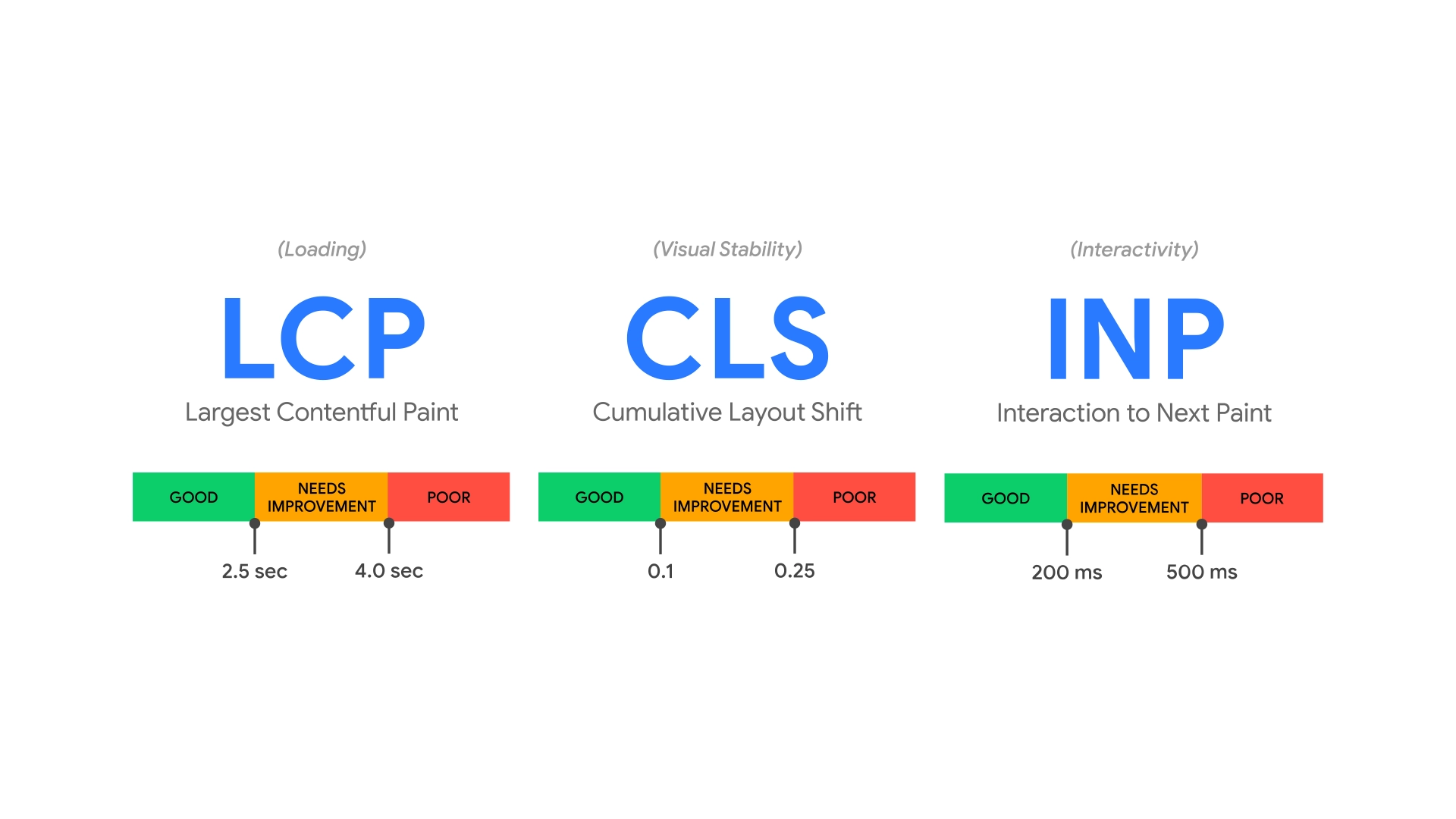
1. Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures page loading performance, evaluating the assets and elements which load across your pages. LCP should occur within 2.5 seconds of when the page first starts loading.
2. First Input Delay (FID): Measures interactivity and how quickly the elements on your page can be accessed. Pages should have an FID of less than 100 milliseconds to be effective.
3. Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability. Pages should maintain a CLS of less than 0.1 to have a positive impact on your site.
43% of mobile URLs and 44% of desktop URLs pass the Largest Contentful Paint benchmark of 2.5 seconds
Why Core Web Vitals Matter for SEO
Google has made it clear throughout many public statements and published documents that user experience is a priority for them, their users and for their future platforms. Core Web Vitals directly impacts how users perceive your site and the level of satisfaction they have when using it. A site that loads fast, responds promptly to user interactions quickly, and remains stable as it loads (doesn’t break), will likely retain users for a longer period of time and reduce bounce rates throughout. This, in turn, signals to Google that your site is a valuable source of content, which is optimised to provide the best possible user experience, and thus should rank higher in search results over sites which aren’t.

Steps to Improve Core Web Vitals
1. Optimise Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
Optimise Images
Compress and Resize: Use modern formats for your images, like WebP and tools like ImageOptim or TinyPNG or even Photoshop being able to compress images without losing quality.
Lazy Loading: Implement lazy loading to your image libraries so that images only load when they come into the view on the page by a user. This reduces the initial loading time.
Improve Server Response Times
Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN): Distribute your content globally to reduce latency. This can be achieved by using a CDN which ensures your assets can be loaded from various parts of the globe to reduce loading times. E.g your content could load from Europe to ensure better performance for these users.
Optimise Server Performance: Upgrade your hosting plan or optimise your backend code and database queries. Upgrading things like your hosting will ensure your site loading times and speed is optimised and serves your users better.
Minimise CSS and JavaScript
Minify and Combine Files: Use tools like CSSNano and UglifyJS to reduce file sizes. Reducing spaces and unnecessary code from your files will help to reduce the overall loading times.
Asynchronous Loading: Load non-critical JavaScript files asynchronously to prevent render-blocking and enhance your overall site speeds.
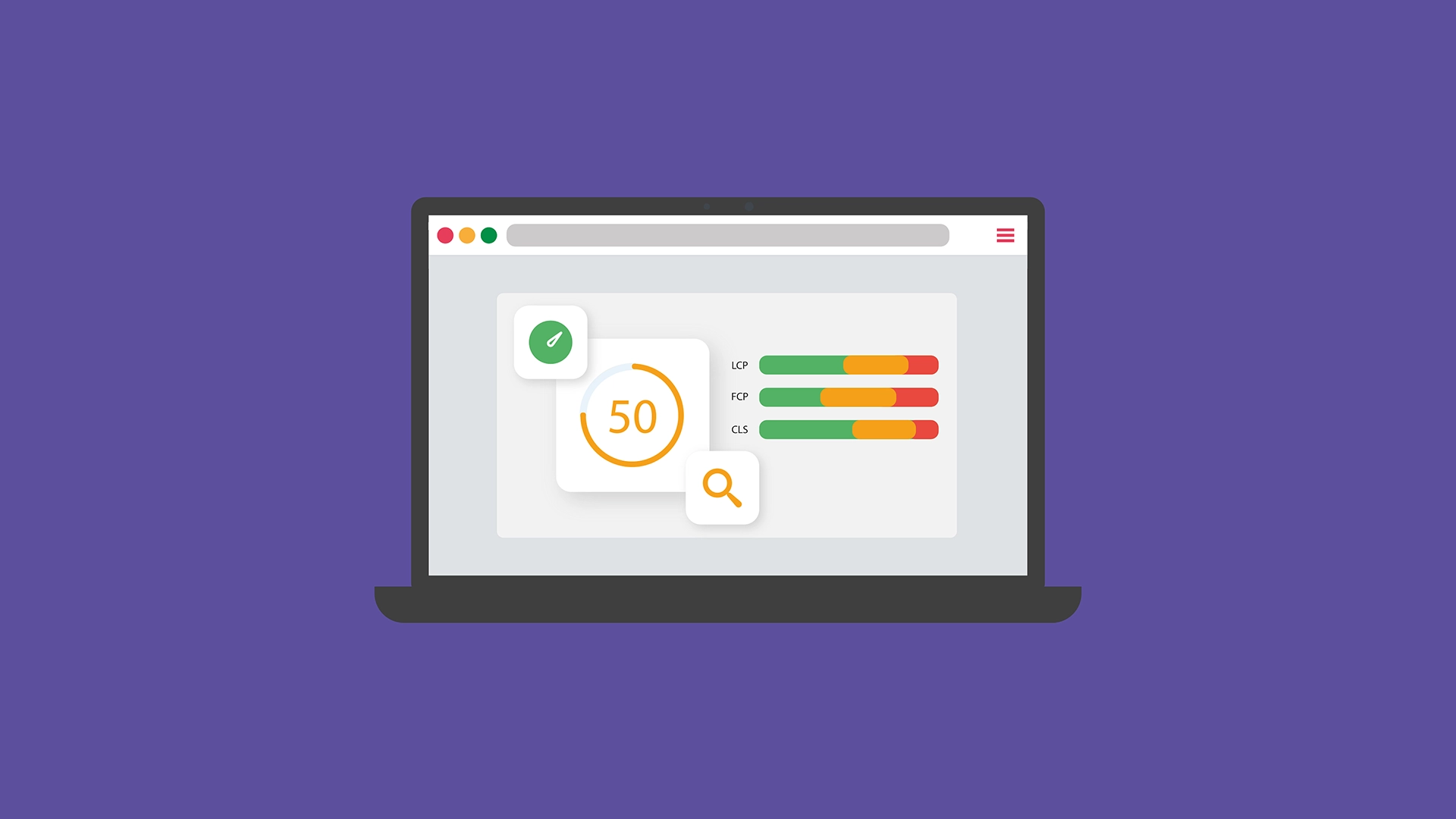

2. Enhance First Input Delay (FID)
Reduce JavaScript Execution Time
Code Splitting: Break down your JavaScript code into smaller, manageable chunks. For example, splitting third party code and your own code from your site will enable each set to be loaded independently and thus load faster.
Optimise Third-Party Scripts and Plug-ins
Monitor and Manage: Regularly audit third-party services, scripts and plugins, validating each one and then removing any that are not essential to your website.
Asynchronous Loading and Deferred Loading: Load third-party scripts asynchronously will help to reduce your overall loading times and FID. You could also defer them to improve page load times too.

3. Improve Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
Set Size Attributes for Media
Specify Dimensions: Always set width and height attributes for all of your images and video files across your site to reserve space and ensure optimised images and videos. This helps to rescue pixelation across your media files by setting a standard loading ratio.
CSS Aspect Ratio: Use CSS aspect ratio boxes to ensure proper space allocation between your content, elements on page, images and videos. This is particularly useful for responsive layouts and mobile views.
Ensure Fonts Load Properly
Font Loading Strategies: Use font-display: swap; to prevent invisible text during loading. This helps to retain users by showing that your content is in fact visible during load, to help show the user it is working and to improve perceived loading times.
Limit Web Fonts: Reduce the number of web fonts and avoid complex font setups to ensure all of the wording and text across your site loads fast and in the correct formats. Complex fonts can also take longer to load, and thus increase the page loading times for users.
Stabilise Dynamic Content
Reserve Space for Ads and Embeds: Allocate space across your website for ads and embeds in advance to prevent cumulative shifts. Using ad placeholders is perfect for this to ensure a reduction in layout shifts and dynamic content.
Avoid Injecting Content Above Existing Content: Add new content below existing content or in reserved spaces. This will help to reduce the likelihood that the new content will cause issues to the already existing content on the page or site.
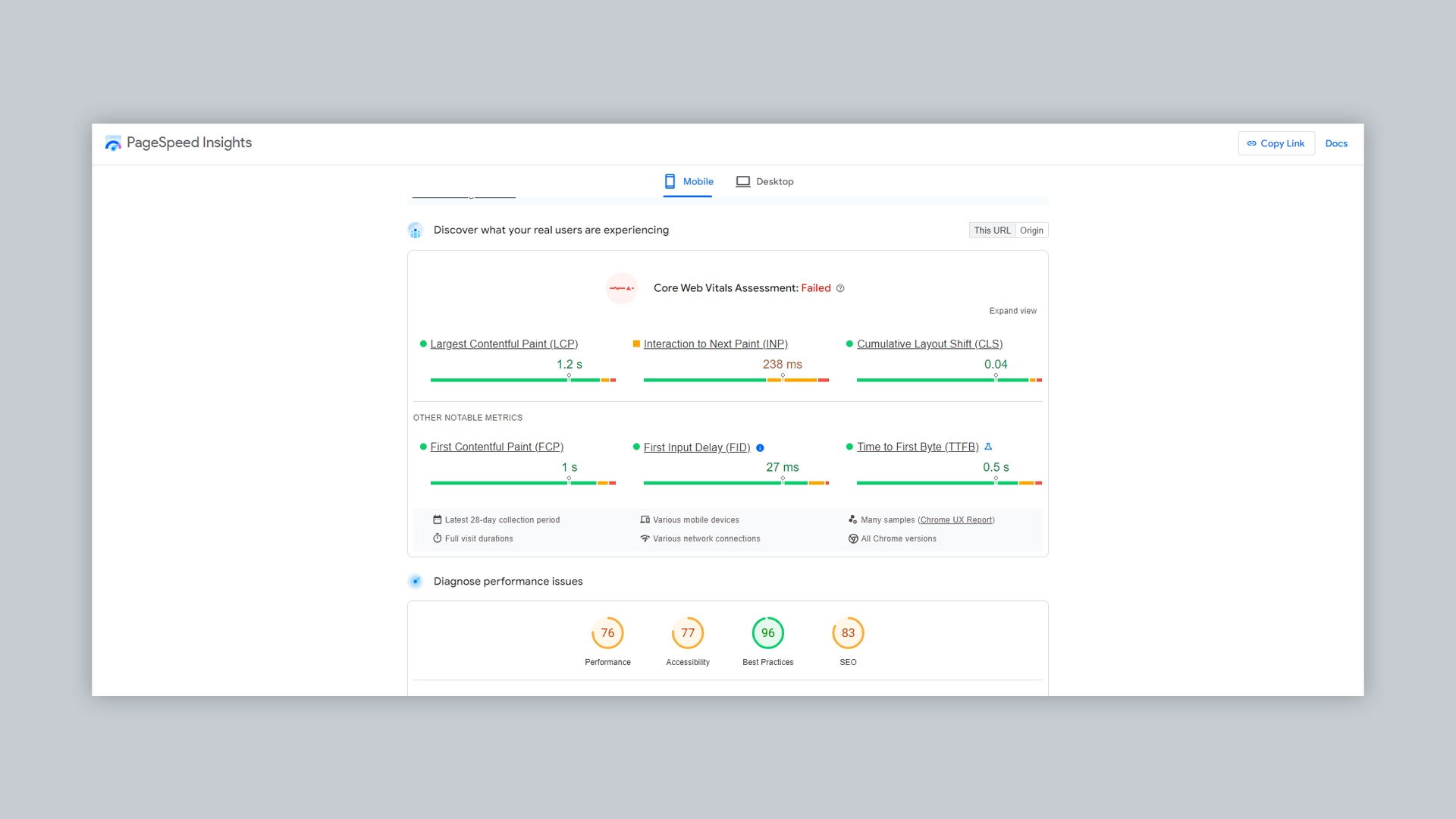
Tools to Monitor and Improve Core Web Vitals
You can use a wide range of different tools to improve your core web vital scores:
Google PageSpeed Insights: Provides a detailed analysis into your website loading performance and also provides a range of suggestions to improve your Core Web Vitals scores.
Lighthouse: An open-source tool developed by Google that runs various audits for your website or any website that is entered, including Core Web Vitals. This tool aims at not only improving site speed, but also helps to improve the overall page experience.
Web Vitals Chrome Extension: Monitors Core Web Vitals in real-time as you browse your site. This will help you to identify issues with your Core Web Vitals in real time and allow you to identify individual pages and components which are causing the issues.
Thoughts...
Improving your Core Web Vitals scores and measuring the change to enable you to optimise your site continuously is crucial to SEO success. However, it is not just about better SEO rankings; it’s about providing a superior user experience to your users which in turn will be looked on favourably in SERPs. By continually focusing on optimising the three main areas of your Core Web Vitals (LCP, FID, and CLS), you can ensure your website is fast, responsive, secure and stable, keeping users engaged and satisfied for longer.
More interesting content...
Like this story? Share it on your social media...
For more of the latest content, why not subscribe to our mailing list...